Welcome to Hipofly Shipping Company’s comprehensive guide on regulatory documents for international shipping from China. Navigating the world of global trade demands a firm grasp of essential documents that facilitate the movement of goods across borders. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or new to international commerce, this guide will serve as your invaluable resource.
At Hipofly Shipping Company, we understand the critical role that regulatory documents play in ensuring smooth international trade operations. We’re dedicated to simplifying this process for you, offering guidance on three fundamental documents integral to shipping from China:
- China Customs Declaration: Explore its significance and its importance for imports into China, customs clearance, and compliance with regulations.
- Certificate of Origin (CO): Discover how it certifies the source of goods and impacts trade agreements and customs procedures.
- Export License: Uncover Export Licenses’ complexities and their role in authorizing the legal export of specific goods and technologies.
Throughout this guide, we’ll provide insights, explanations, and practical examples to help you grasp these crucial documents. Whether you’re expanding your market reach or ensuring regulatory compliance, we’re here to simplify the complexities of global trade and support your success.
What is a China Customs Declaration?
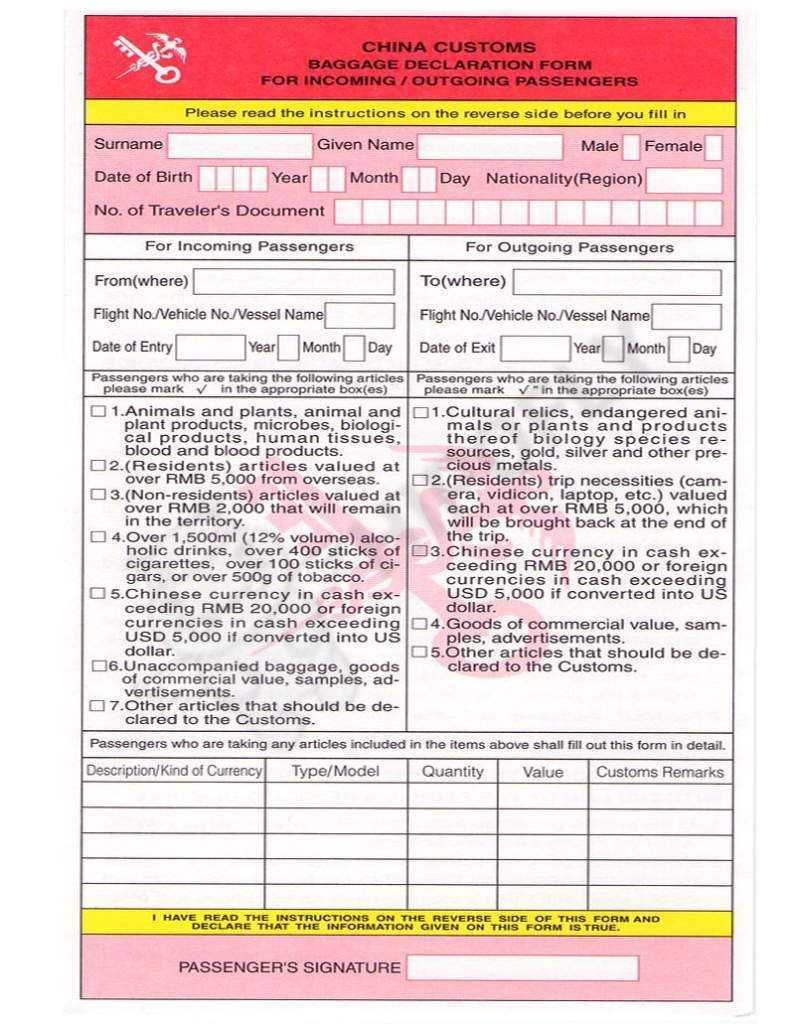
A China Customs Declaration is a vital Regulatory Document for shipping from China. It is a formal submission made to Chinese customs authorities, providing essential information about the cargo being shipped. The importance of this document lies in its role as a gateway for international shipments. It ensures compliance with trade regulations, expedites customs clearance, and ultimately enables goods to move seamlessly from China to destinations worldwide. Without a properly filed China Customs Declaration, shipping processes can be hindered, leading to delays, legal issues, and potential penalties. It’s a foundational document that keeps the global shipping network running smoothly.
Key Components of a China Customs Declaration
The key components of a China Customs Declaration include:
- Goods Description: A detailed description of the goods being shipped, including their type, quantity, weight, and dimensions.
- Value of Goods: The declared value of the goods, which is essential for customs duty assessment and valuation.
- Origin of Goods: Information about where the goods were manufactured or produced, which is crucial for determining preferential trade agreements and tariff rates.
- Exporter Information: Details about the exporter, including their name, address, and contact information.
- Importer Information: Information about the importer in the destination country, including their name, address, and contact details.
- Shipping Information: Details about the mode of transportation, the route, and the expected arrival date at the destination.
- Customs Codes: The appropriate customs codes (Harmonized System Codes) that classify the goods for customs purposes.
- Invoices and Supporting Documents: Copies of commercial invoices, packing lists, and any other documents that validate the shipment’s accuracy and authenticity.
- Declaration Signatures: Signatures of authorized representatives, including the exporter and customs officials, certifying the accuracy of the information provided.
- Compliance Statements: Statements confirming that the shipment complies with all relevant customs and trade regulations.
These components collectively ensure that the China Customs Declaration provides accurate and complete information about the goods being exported, facilitating a smooth and compliant international shipping process.
Advantages of China Customs Declaration
The China Customs Declaration offers several advantages for businesses and individuals involved in international trade and shipping:
- Legal Compliance: One of the primary advantages is that it helps businesses comply with Chinese and international trade laws and regulations. Accurate declarations ensure that shipments meet all legal requirements, reducing the risk of customs violations, fines, or delays.
- Smooth Customs Clearance: Properly completed customs declarations expedite the customs clearance process. This means that goods can move more quickly through customs checkpoints, reducing the time spent waiting for clearance and the associated storage costs.
- Tariff Determination: It allows customs authorities to determine the appropriate tariffs and duties that must be paid on imported or exported goods. This ensures that importers and exporters are aware of the financial implications of their shipments in advance.
- Customs Valuation: Customs declarations help establish the value of goods for taxation purposes, ensuring that duties and taxes are calculated accurately based on the declared value of the goods.
- Trade Facilitation: The China Customs Declaration contributes to the facilitation of international trade by providing a standardized and transparent process for documenting shipments. This transparency can help build trust between trading partners and governments.
- Data for Trade Statistics: The information collected through customs declarations is used to compile trade statistics, which are essential for analyzing economic trends, making informed policy decisions, and identifying emerging market opportunities.
- Risk Management: Customs declarations also play a role in customs risk management programs. Customs authorities can use this data to identify high-risk shipments or potential smuggling attempts, enhancing border security.
- Documentation for Disputes: In case of disputes or discrepancies, customs declarations serve as a critical reference point. They provide an official record of the details of the shipment, helping resolve disputes between parties involved in international trade.
- Compliance with Trade Agreements: For countries with international trade agreements, customs declarations ensure that goods meet the rules of origin and other criteria specified in those agreements to benefit from preferential tariff rates.
- Global Trade Integration: By adhering to international customs standards and practices, China Customs Declarations contribute to the seamless integration of China’s trade with the global economy, promoting international trade relations.
In summary, the China Customs Declaration is a crucial document that offers various advantages, including legal compliance, efficient customs clearance, accurate taxation, and support for international trade. Businesses and individuals benefit from its role in facilitating smooth cross-border transactions and maintaining transparency in the global supply chain
Disadvantages and Limitations of China Customs Declaration
While the China Customs Declaration is an essential document for international trade, it also comes with certain disadvantages and limitations:
- Complexity: Filling out a customs declaration can be a complex and time-consuming process, especially for businesses dealing with a wide range of products or frequent shipments. Navigating the customs codes and regulations can be challenging, leading to errors or delays.
- Language Barriers: Language differences can pose a challenge when completing customs declarations, particularly for businesses or individuals who are not proficient in Chinese. Accurate translation and interpretation may be necessary.
- Documentation Requirements: Customs authorities often require a variety of supporting documents, such as invoices, certificates of origin, and packing lists, to accompany the declaration. Gathering and organizing these documents can be cumbersome.
- Inaccuracies and Errors: Mistakes or inaccuracies in customs declarations can lead to customs audits, delays, fines, or even the seizure of goods. Ensuring the accuracy of information is crucial, but human errors can still occur.
- Customs Delays: Customs authorities may subject shipments to inspections or hold them for various reasons, such as suspicious contents or incomplete documentation. These delays can disrupt supply chains and increase costs.
- Trade Tariffs and Duties: For businesses, customs declarations mean the potential payment of trade tariffs and import/export duties, which can significantly impact the cost of doing business and affect profit margins.
- Trade Barriers and Regulations: Customs declarations must adhere to various trade barriers and regulations, including import quotas, trade embargoes, and product-specific restrictions. Navigating these regulations can be challenging.
- Risk of Audits: Customs authorities may audit customs declarations at random or based on specific criteria. An audit can be time-consuming and may result in penalties if discrepancies are found.
- Data Security: The information provided in customs declarations contains sensitive business and trade data. Ensuring the security and confidentiality of this data is a constant concern, especially in the era of cyber threats.
- Costs: Businesses may incur costs related to customs declaration preparation, including hiring customs brokers or specialists to navigate complex regulations and ensure compliance.
- Trade Disputes: In some cases, disputes may arise between importers, exporters, and customs authorities regarding the accuracy or validity of customs declarations, leading to potential legal issues.
- Limitations in Digitalization: While many countries are moving towards digital customs declarations, some regions or smaller ports may still rely on paper-based processes, leading to inefficiencies and potential delays.
In summary, while the China Customs Declaration is a fundamental document for international trade, its disadvantages and limitations stem from the complexity of customs processes, potential errors, trade barriers, and the need for strict adherence to regulations. Businesses must navigate these challenges to ensure the smooth flow of goods across borders.
Case Study: Application of a China Customs Declaration
In this section, we present a concise overview of the key steps undertaken by XYZ Company to effectively apply China Customs Declarations in their international trade operations. Facing the challenges of navigating complex customs regulations and ensuring compliance, XYZ Company adopted a proactive approach, resulting in smoother customs processes, reduced risks, and enhanced global business operations. Below, you will find a structured table outlining the specific actions taken and the subsequent results achieved by XYZ Company.
| Step | Action Taken by XYZ Company |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Hired customs experts and brokers. |
| Step 2 | Invested in customs declaration software. |
| Step 3 | Implemented a centralized document system. |
| Step 4 | Maintained open communication with brokers and customers. |
| Step 5 | Conducted customs compliance training for employees. |
Results:
- Efficiency: Faster customs clearance.
- Risk Reduction: Minimized fines and audits.
- Cost Savings: Avoided unnecessary expenses.
- Customer Relations: Improved client satisfaction.
- Global Expansion: Enhanced market reach.
This table encapsulates the proactive measures undertaken by XYZ Company to navigate the complexities of customs procedures, showcasing the positive impact on their international trade operations.
What is a Certificate of Origin (CO)?
A Certificate of Origin (CO) is a crucial international trade document that certifies the country of origin of goods in a particular shipment. It serves as an official declaration by the exporter or manufacturer, affirming that the products being exported originate from a specific country or region. The CO provides important information about the origin of the goods and is typically issued and authenticated by a recognized authority, such as a chamber of commerce or a government agency responsible for trade.
The Certificate of Origin is important for several reasons:
- Tariff Determination: Customs authorities in the importing country use the CO to determine the applicable tariffs and trade agreements that govern the imported goods. Different trade agreements or tariff schedules may apply to products from different countries.
- Preferential Treatment: Some countries have preferential trade agreements with others, granting reduced tariffs or duty-free access to goods from specific regions. The CO helps goods qualify for such preferential treatment.
- Quality and Authenticity: The CO provides assurance to the importing country that the goods are indeed of the claimed origin. This helps prevent misrepresentation or fraud in international trade.
- Statistical Data: Customs authorities use data from Certificates of Origin to compile trade statistics, which are essential for tracking international trade trends and making informed policy decisions.
- Trade Barriers: Certain countries may impose trade barriers or restrictions on goods from specific regions. The CO helps businesses navigate these barriers by proving the origin of their products.
In summary, a Certificate of Origin is a fundamental document in international trade that establishes the origin of goods, facilitates customs clearance, and enables access to preferential trade agreements. It plays a crucial role in determining applicable tariffs and ensuring compliance with trade regulations.

Advantages of Utilizing a Certificate of Origin
For Buyers:
Buyers in international trade benefit from the utilization of a Certificate of Origin (CO) in the following ways:
- Tariff Reduction and Cost Savings: COs allow buyers to enjoy reduced tariffs or even duty-free access to certain markets. This translates to cost savings on imported goods, making products more affordable for consumers.
- Quality Assurance: A CO serves as evidence of the product’s origin, providing assurance to buyers that they are receiving genuine, high-quality goods from a specific region or country.
- Legal Compliance: Buyers can confidently demonstrate compliance with customs regulations by presenting a valid CO, minimizing the risk of customs-related delays or complications.
- Market Access: In some cases, certain markets impose restrictions or requirements based on product origin. A CO enables buyers to access these markets and expand their product offerings.
- Transparent Supply Chains: COs help buyers track the origin of components or materials used in manufacturing, ensuring transparency in their supply chains and adherence to labeling requirements.
For Sellers:
Sellers in international trade benefit from the utilization of a Certificate of Origin (CO) in the following ways:
- Tariff Advantages: COs provide sellers with a competitive edge by making their products eligible for reduced tariffs or preferential trade agreements. This can lead to cost savings and potentially lower prices for consumers.
- Market Expansion: With COs in place, sellers can explore new markets and reach a broader customer base by meeting origin requirements specified by importing countries.
- Risk Mitigation: COs act as safeguards against potential legal issues or disputes related to product origin, as they provide clear documentation and transparency.
- Consumer Trust: COs enhance consumer confidence in the authenticity of products, which can lead to increased sales and brand loyalty.
- Data for Strategy: Sellers can use information from COs to analyze trade trends, identify emerging market opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions.
- Trade Agreement Benefits: COs ensure that goods meet the rules of origin stipulated in trade agreements, allowing sellers to fully leverage the benefits of these agreements.
In summary, buyers and sellers in international trade both benefit from the use of a Certificate of Origin, with buyers enjoying cost savings, quality assurance, and market access, while sellers gain competitive advantages, risk mitigation, and market expansion opportunities. This essential document plays a pivotal role in facilitating smooth and transparent global trade.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Commercial Invoice
Disadvantages for Buyers and Sellers:
- Administrative Burden: Obtaining and verifying COs can be administratively burdensome and time-consuming for both buyers and sellers. It involves gathering documentation and coordinating with authorities.
- Costs: Acquiring COs may incur additional costs, including fees for certification and processing. These costs can add to the overall expenses of the trade transaction.
- Counterfeit COs: In some cases, counterfeit or fraudulent COs may be presented, leading to potential issues related to the authenticity of the product’s origin.
- Limited Applicability: COs are primarily relevant for certain industries and products. Not all goods require or benefit from a CO, which can limit its utility for some businesses.
Disadvantages for Buyers:
- Increased Costs: While COs can lead to cost savings through reduced tariffs, the added administrative and certification costs may offset these savings, particularly for small-scale buyers.
- Complexity: Understanding and navigating the specific requirements and regulations related to COs for various countries and industries can be complex and challenging for buyers.
- Verification Challenges: Buyers may face difficulties in verifying the authenticity and accuracy of COs, especially if they are unfamiliar with the issuing authority or the document’s format.
Disadvantages for Sellers:
- Market Access Barriers: Some markets may impose stringent CO requirements or restrict the entry of products without a valid CO. Sellers may encounter challenges entering these markets.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Failure to provide a valid CO can put sellers at a competitive disadvantage in markets where such certificates are the norm or where preferential trade agreements apply.
- Compliance Risks: Sellers may inadvertently misinterpret or misapply CO requirements, leading to non-compliance with customs regulations and potential legal issues.
- Market Limitations: Relying heavily on COs can limit sellers’ market reach, as not all customers or markets may require or recognize the significance of a CO.
Case Study: Application of a Certificate of Origin
Background:
XYZ Trading Co., a textile importer in the United States, faced challenges in customs compliance and cost savings for their textile imports.
Solution
| Step | Action Taken by XYZ Trading Co. |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Conducted market research to identify countries eligible for trade agreements. |
| Step 2 | Collaborated with suppliers to gather necessary documents: invoices, packing lists, and manufacturing data. |
| Step 3 | Obtained Certificates of Origin (COs) from the local chamber of commerce for eligible textiles. |
| Step 4 | Ensured complete and accurate customs documentation, including COs, to prevent customs delays. |
| Step 5 | Educated customers on the significance of COs, enhancing trust and transparency. |
Results:
- Tariff Savings: Reduced tariffs on textiles, leading to cost savings.
- Transparent Supply Chain: Enhanced customer trust and product transparency.
- Compliance Assurance: Avoided customs complications and fines.
- Market Expansion: Expanded into new markets.
- Competitive Edge: Gained a competitive advantage with verifiable product origins.
This case highlights how XYZ Trading Co. strategically applied Certificates of Origin to streamline their international trade operations and achieve tangible benefits
What’s an Export License?
An Export License is a legally mandated authorization issued by a government authority that grants individuals, businesses, or entities the lawful permission to export specific goods or technologies to other countries or destinations. The issuance of Export Licenses is a crucial regulatory mechanism in international trade, serving to control and monitor the movement of goods, protect national security interests, and ensure compliance with trade regulations.
In the context of shipping goods from China to worldwide destinations, utilizing Export Licenses holds significant importance for several key reasons:
- Compliance with International Regulations: Shipping goods across international borders involves navigating complex and diverse sets of regulations, including those related to customs, trade agreements, and security. Export Licenses help ensure that shipments from China adhere to these regulations, mitigating the risk of customs delays, fines, or legal complications.
- Control of Sensitive Technologies: Export Licenses are essential for controlling the export of sensitive technologies or goods that have both civilian and military applications, known as “dual-use” items. China, as a significant exporter, often deals with these types of goods. Obtaining an Export License ensures that such items are exported in accordance with security and foreign policy objectives.
- Customs Clearance Facilitation: Many countries require valid Export Licenses as part of the customs clearance process. Without the proper license, shipments may be held up at customs, causing delays that can disrupt supply chains and lead to financial losses.
- Trade Sanctions and Embargoes: International trade is subject to trade sanctions and embargoes imposed by various countries and international bodies. Export Licenses help ensure that shipments from China do not violate these sanctions, which can have severe legal and financial consequences.
- Market Access: Certain countries have preferential trade agreements in place that grant reduced tariffs or duty-free access to goods from specific regions, including China. Export Licenses are necessary to prove the origin of goods and take advantage of these trade preferences, potentially reducing import costs for the destination countries.
- National Security and Foreign Policy: Export Licenses enable governments to implement national security and foreign policy objectives by controlling the export of specific goods to certain countries or entities. By adhering to these licensing requirements, businesses can avoid potential conflicts with international relations.
- Legal Consequences: Non-compliance with export control regulations, including the absence of required Export Licenses, can lead to legal repercussions, such as fines or export restrictions. Using Export Licenses helps businesses avoid these consequences and maintain their reputation.
In summary, an Export License is an essential component of international trade when shipping goods from China to worldwide destinations. It ensures compliance with regulations, promotes transparency, and helps prevent potential legal and logistical challenges that can arise in the complex landscape of global commerce. Businesses engaged in international trade must carefully adhere to these licensing requirements to ensure smooth and lawful shipping operations.
Key Components of a Export License
The key components of an Export License typically include the following information and details:
- Exporter Information: Details about the exporter, including the company’s name, address, contact information, and tax identification or registration number.
- Importer Information: Information about the importer or consignee in the destination country, including their name, address, and contact details.
- License Number: A unique identification number assigned to the export license for reference and tracking purposes.
- Date of Issue: The date when the export license was issued by the relevant government authority.
- Description of Goods: A detailed description of the goods being exported, including their quantity, type, specifications, and any relevant product codes or classifications (e.g., ECCN or USML categories for controlled items).
- Destination Country: The country or countries to which the goods are authorized for export.
- Export Control Information: Information specifying any export controls or restrictions applicable to the goods. This may include details about licensing requirements, end-user restrictions, and potential use in prohibited activities.
- Validity Period: The period during which the export license is valid and can be used for exporting the specified goods. It is important to ensure that the export occurs within this timeframe.
- Authorized Signatures: Signatures of authorized personnel, such as government officials or export control officers, certifying the authenticity of the export license.
- Additional Conditions: Any additional conditions or requirements imposed by the issuing authority. These conditions may include reporting obligations, record-keeping requirements, or specific instructions related to the export.
- End-User and End-Use Information: Some export licenses may require information about the intended end-user and the intended use of the exported goods. This helps ensure that the goods are not diverted to unauthorized or prohibited uses.
- Value and Currency: The declared value of the goods and the currency in which the transaction is denominated. This information may be necessary for customs and trade statistics.
- Exporting Method: Details about the method of transportation or shipment of the goods, including the mode of transportation, shipping route, and any related shipping documents.
- Re-export Restrictions: If applicable, information about any restrictions on re-exporting the goods to other countries or entities.
License Conditions: Specific conditions or limitations associated with the use of the export license, such as restrictions on the quantity or frequency of exports.
It’s important to note that the specific content and format of export licenses may vary depending on the exporting country’s regulations, the nature of the goods being exported, and the destination country’s requirements. Exporters must ensure full compliance with all conditions specified in the export license to avoid legal consequences and facilitate smooth international trade operations.

Advantages of Export License
The advantages of obtaining an Export License in international trade are significant and include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with national and international export regulations and laws, which helps prevent legal issues, fines, and penalties for unauthorized exports.
- National Security: Facilitating government oversight and control over the export of sensitive goods, technologies, and military equipment to protect national security interests.
- Foreign Policy Objectives: Allowing governments to enforce foreign policy objectives, such as restricting exports to certain countries or entities, supporting diplomatic goals, or responding to international events.
- Trade Facilitation: Streamlining the export process by providing clear guidelines, rules, and conditions for the export of specific items, which helps businesses navigate international trade regulations more effectively.
- Customs Clearance: Assisting with customs clearance in the destination country, as many countries require a valid Export License as part of the customs documentation.
- Market Access: Enabling exporters to access markets with preferential trade agreements that may require proof of origin or other export documentation to benefit from reduced tariffs or duty-free access.
- Protection of Intellectual Property: Helping protect intellectual property rights by regulating the export of patented or copyrighted technologies, preventing unauthorized replication abroad.
- Preventing Illicit Trade: Combating illicit trade by restricting the export of goods that can be used for illegal activities, such as weapons trafficking, narcotics distribution, or counterfeiting.
- Transparency: Providing transparency in international trade transactions by documenting the export of specific items and their intended end-users and end-uses.
- Global Supply Chain Management: Enabling businesses to manage complex global supply chains more effectively by adhering to export controls and ensuring products reach their intended destinations.
- Legal Consequences: Protecting exporters from legal consequences and liabilities associated with unauthorized or non-compliant exports.
- Data Collection: Assisting governments in collecting trade data and statistics, which are valuable for understanding trade trends, shaping economic policies, and identifying growth opportunities.
- Competitive Advantage: Giving compliant exporters a competitive advantage by allowing them to access markets, secure contracts, and participate in industries with stringent export control requirements.
In summary, Export Licenses offer various advantages for businesses engaged in international trade, ranging from legal compliance and national security to market access and competitive positioning. They play a critical role in facilitating responsible and regulated global commerce while ensuring that sensitive items and technologies are appropriately controlled and monitored.
Disadvantages of Export License
While Export Licenses serve important regulatory and security purposes in international trade, they also come with certain disadvantages and challenges, including:
- Administrative Burden: The process of applying for and obtaining Export Licenses can be time-consuming and administratively complex, requiring extensive paperwork, documentation, and coordination with government authorities.
- Costs: Export Licenses may incur additional costs, including application fees, compliance-related expenses, and legal consulting fees, which can increase the overall cost of exporting.
- Delays in Exporting: The licensing process can introduce delays in the export timeline, potentially affecting supply chains, customer deliveries, and contract fulfillment.
- Loss of Competitive Advantage: In markets where competitors are not subject to the same export controls, Export Licenses can put exporters at a disadvantage due to added costs and time delays.
- Risk of License Denial: There is always the risk that an Export License application may be denied, particularly for sensitive goods or destinations, which can disrupt planned export activities.
- Complexity and Ambiguity: Export controls and regulations can be complex and subject to change. Businesses may struggle to interpret and navigate evolving export requirements.
- Limited Market Access: Some countries impose strict export controls on certain goods, limiting the export opportunities for businesses in those industries.
- Market Entry Barriers: For businesses seeking to enter new markets, export licensing requirements may create barriers to entry, particularly if the process is unfamiliar or difficult to navigate.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Stringent export controls can disrupt supply chains, particularly for businesses with complex global sourcing and distribution networks.
- Trade Sanctions and Embargoes: Export Licenses may be subject to trade sanctions and embargoes, preventing exports to specific countries or entities, which can impact market expansion.
- Counterfeit Documents: Exporters may encounter counterfeit or fraudulent Export Licenses, potentially leading to legal and reputational risks.
- End-User Verification: Ensuring that exported goods are used by the authorized end-users and for the intended end-uses can be challenging and may require ongoing monitoring and due diligence.
- Market Limitations: Relying heavily on Export Licenses can limit the scope of markets and customers that a business can engage with, particularly if the goods are subject to stringent controls.
In summary, while Export Licenses are necessary for ensuring compliance with export regulations and protecting national security interests, they can also introduce complexities, costs, and delays into the export process. Exporters must carefully navigate these challenges to maintain regulatory compliance while minimizing their impact on trade operations.
Case Study: Application of a Export Licenses
Background:
XYZ Electronics, a global electronics manufacturer specializing in semiconductors, faced the challenge of expanding its market while complying with strict export control regulations.
Solution:
| Step | Action Taken by XYZ Electronics |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Conducted a compliance assessment of export control regulations in Country A (home country), Country B, and Country C (target markets). |
| Step 2 | Classified products according to ECCN or USML, determining their export control status. |
| Step 3 | Identified and verified end-users and end-uses to ensure compliance and prevent unauthorized diversion. |
| Step 4 | Submitted comprehensive license applications to the relevant government authorities for exports to Country B and Country C. |
| Step 5 | Established strict internal compliance procedures, including employee training, record-keeping, and audits. |
| Step 6 | Implemented ongoing monitoring and reporting mechanisms for export activities. |
Results:
- Market Expansion: Successfully entered new markets, expanding customer base and revenue.
- Compliance: Maintained strict adherence to export control regulations, avoiding legal and reputational risks.
- Enhanced Reputation: Gained industry and customer trust through transparency and diligence in compliance.
- Risk Mitigation: Mitigated the risk of unauthorized diversion of technology.
- Sustainable Growth: Achieved sustainable growth by balancing expansion and compliance.
This case illustrates how XYZ Electronics effectively navigated the complexities of export licensing to expand its global market presence while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Comparison Between China Customs Declaration, Certificate of Origin (CO), Export Licenses
Here’s a detailed comparison between the China Customs Declaration, Certificate of Origin (CO), and Export Licenses in international trade:
| Aspect | China Customs Declaration | Certificate of Origin (CO) | Export License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Declaration of imported goods to Chinese customs authorities. | Certifies the country of origin of goods, often for trade agreements and customs purposes. | Legal authorization for exporting specific goods or technologies to foreign countries. |
| Issuing Authority | Chinese customs authorities. | Issued by authorized chambers of commerce or government agencies. | Issued by relevant government authorities in the exporter's country. |
| Components | Information about the imported goods, including their description, value, and origin. | Details about the origin of the goods, including their source and production process. | Details about the exporter, importer, goods, destination, and compliance with regulations. |
| Importance for Shipping | Necessary for customs clearance and compliance with import regulations in China. | May be required for preferential trade agreements and duty reduction in the destination country. | Essential for compliance with export control regulations, ensuring legal export of specific goods. |
| Role in Customs Clearance | Facilitates the smooth clearance of imported goods through Chinese customs. | May be used by customs authorities in the destination country to determine tariff rates. | Critical for demonstrating that the export complies with national security and foreign policy objectives. |
| Typical Use Cases | Required for all imported goods into China. | Commonly used when claiming preferential trade agreement benefits or confirming product origin. | Needed when exporting controlled goods, sensitive technologies, or goods subject to trade sanctions. |
| Impact on Tariffs and Duties | Does not directly affect tariffs or duties but influences customs procedures. | May lead to reduced tariffs or duty exemptions in certain trade agreements. | Does not impact tariffs directly but may be required for goods eligible for reduced tariffs. |
| Authentication | May require official stamps and seals by customs authorities. | Often issued by chambers of commerce or government bodies with official authentication. | Issued by government authorities and typically has legal weight. |
| Scope of Applicability | Specific to imports into China. | Typically related to the country of origin and trade agreements. | Applicable to exports from the exporter's country. |
Differences in Purpose and Scope
| Aspect | China Customs Declaration | Certificate of Origin (CO) | Export License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Declaration of imported goods to Chinese customs authorities. | Certifies the country of origin of goods, often for trade agreements and customs purposes. | Legal authorization for exporting specific goods or technologies to foreign countries. |
| Scope of Applicability | Specific to imports into China. | Typically related to the country of origin and trade agreements. | Applicable to exports from the exporter's country. |
| Primary Function | Facilitates customs clearance and compliance for imported goods. | Confirms the origin of goods, often for tariff purposes and trade agreement benefits. | Ensures compliance with export control regulations for specified goods. |
| Issuing Authority | Chinese customs authorities. | Authorized chambers of commerce or government agencies. | Relevant government authorities in the exporter's country. |
| Key Components | Details about imported goods, their value, and origin. | Information about the origin of goods, including source and production process. | Information about exporter, importer, goods, destination, and regulatory compliance. |
| Impact on Tariffs/Duties | Does not directly affect tariffs/duties but influences customs procedures. | May lead to reduced tariffs/duties in certain trade agreements. | Does not affect tariffs/duties directly but may be required for tariff reductions on eligible goods. |
| Authentication | May require official stamps/seals by customs authorities. | Often issued with official authentication by chambers of commerce/government bodies. | Issued by government authorities, typically with legal weight. |
| Typical Use Cases | Mandatory for all imports into China. | Commonly used in trade agreements or to confirm product origin. | Necessary for controlled/sensitive exports, compliance with sanctions. |
| Role in Customs Clearance | Essential for the smooth clearance of imported goods through Chinese customs. | May be used by customs authorities in the destination country for tariff determination. | Critical for demonstrating compliance with national security and foreign policy objectives. |
Conclusion
In the realm of international trade, understanding and effectively utilizing regulatory documents are paramount to success. In this guide, presented by Hipofly Shipping Company, we have navigated the intricate landscape of three essential documents for shipping from China: the China Customs Declaration, Certificate of Origin (CO), and Export License.
These documents serve as the backbone of international trade, ensuring compliance with regulations, facilitating customs clearance, and supporting your business’s growth and expansion into new markets. Whether you are a seasoned importer/exporter or embarking on your first international trade venture, a firm grasp of these documents is invaluable.
As you venture into the global marketplace, Hipofly Shipping Company is here to provide guidance, simplify complexities, and support your journey in international commerce. With the knowledge gained from this guide, you are better equipped to navigate the challenges and opportunities of international shipping from China.
We invite you to leverage this newfound understanding and embark on your international trade ventures with confidence. May your business thrive on the global stage, and may these regulatory documents be your trusted allies in your quest for success. Hipofly Shipping Company stands ready to assist you on this exciting journey.
The key regulatory documents are the China Customs Declaration, Certificate of Origin (CO), and Export License.
A China Customs Declaration is crucial as it facilitates customs clearance in China and ensures compliance with import regulations.
A Certificate of Origin certifies the country of origin of goods, often leading to reduced tariffs or trade agreement benefits.
Export Licenses are typically required for exporting controlled goods, sensitive technologies, or items subject to trade sanctions.
ou can obtain an Export License by applying to the relevant government authorities in your country and complying with export control regulations.
A Commercial Invoice helps establish the terms of sale, provides a record of the transaction, and assists with customs clearance.
The Certificate of Origin is often required to prove that goods meet the origin criteria for tariff reduction or duty exemption in trade agreements.
Yes, a China Customs Declaration is mandatory for all imported goods entering China.
No, a Certificate of Origin certifies the country of origin of goods, whereas a Certificate of Authenticity confirms the authenticity of a product or its components.
One potential disadvantage is that not all goods are eligible for preferential treatment under trade agreements, limiting their benefits.


